The ignition
system in an automobile plays a crucial role in the proper functioning of the
internal combustion engine. It is responsible for generating and controlling
the spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture within the engine's combustion
chamber, leading to a controlled explosion that generates power to propel the
vehicle. This article will provide an in-depth overview of the ignition
system's function and key components.
The function of the Ignition System
The primary
function of the ignition system is to generate a high-voltage electrical charge
and deliver it to the spark plugs at the appropriate moment during the engine's
operation. This high-voltage charge creates a spark that ignites the compressed
air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber, causing a rapid increase in
pressure and temperature that forces the engine's pistons to move, ultimately
driving the vehicle's wheels.
To achieve
this, the ignition system must perform the following tasks:
1. Generate
a high-voltage electrical charge.
2.
Distribute the charge to the correct spark plug in the correct cylinder.
3. Time the
delivery of the electrical charge to coincide with the optimal point in the
engine's cycle.
The efficiency
and reliability of the ignition system are critical to the overall performance
of the engine, as it directly affects fuel consumption, emissions, and engine
lifespan.
Components of the Ignition System
The ignition
system is composed of several essential components that work together to
generate, control, and deliver the high-voltage electrical charge to the spark
plugs. These components include:
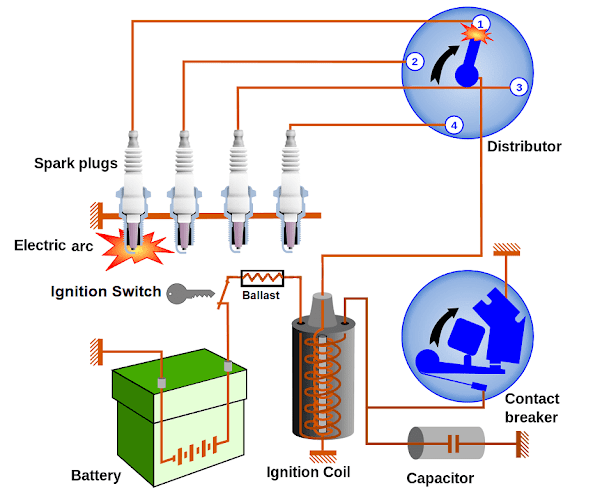
1.
Ignition Switch
The ignition
switch is the starting point of the ignition system, as it allows the driver to
control the flow of electrical power to the engine. When the key is inserted
and turned, the ignition switch connects the battery to the other components of
the ignition system, enabling the engine to start and run.
2.
Battery
The battery
provides the electrical power required for the ignition system to function. It
supplies a low-voltage current (usually 12 volts) that is later transformed
into a high-voltage charge by the ignition coil.
3.
Ignition Coil
The ignition
coil is a crucial component responsible for generating the high-voltage
electrical charge needed to create the spark at the spark plugs. It functions
as a transformer, converting the low-voltage current from the battery into a
high-voltage charge (typically between 20,000 and 50,000 volts). This
high-voltage charge is then sent to the distributor or directly to the spark
plugs, depending on the type of ignition system used.
4.
Distributor
In older
vehicles equipped with a mechanical ignition system, the distributor is
responsible for distributing the high-voltage charge generated by the ignition
coil to the appropriate spark plugs. The distributor consists of a rotating
shaft with a rotor that is connected to the ignition coil. As the shaft
rotates, the rotor makes contact with terminals connected to the spark plug
wires, sending the high-voltage charge to the corresponding spark plug.
5. Spark
Plug Wires
Spark plug
wires are insulated conductors that transfer the high-voltage charge from the
distributor or ignition coil to the spark plugs. They are designed to withstand
high temperatures and resist electrical interference that could disrupt the
proper functioning of the ignition system.
6. Spark
Plugs
Spark plugs
are critical components that deliver the high-voltage electrical charge to the
combustion chamber, creating the spark necessary to ignite the air-fuel
mixture. A spark plug consists of a central electrode, an insulator, and a
ground electrode. The gap between the central electrode and the ground
electrode is where the spark occurs, igniting the air-fuel mixture in the
engine's combustion chamber.
7.
Ignition Control Module (ICM) and Engine Control Module (ECM)
In modern
vehicles, the ignition system is controlled by electronic components, such as
the ignition control module (ICM) and the engine control module (ECM). These
components manage the ignition system's timing, ensuring that the spark plugs
receive the high-voltage charge at the correct moment during the engine's
cycle. This precise control helps optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency,
and emissions.
Types of Ignition Systems
There are
two main types of ignition systems used in automotive engines: mechanical (or
contact breaker) ignition systems and electronic ignition systems.
Mechanical
Ignition System
The
mechanical ignition system, also known as the contact breaker or points
ignition system, is an older technology that relies on mechanical components,
such as the distributor, to generate and control the spark. Although it has
been largely replaced by electronic ignition systems in modern vehicles,
mechanical ignition systems can still be found in older vehicles and classic
cars.
Electronic
Ignition System
Electronic
ignition systems have become the standard in modern vehicles due to their
increased reliability, efficiency, and performance. These systems use
electronic components to control the ignition process, such as the ICM and ECM,
as well as crankshaft and camshaft position sensors to determine the optimal
timing for spark delivery.
There are
two main types of electronic ignition systems:
1.
Distributor-Based Ignition System: This type of system uses an ignition coil to
generate the high-voltage charge, which is then sent to a distributor that
distributes the electrical charge to the appropriate spark plug.
2. Distributor
less Ignition System (DIS): In a DIS system, the ignition coil is connected
directly to each spark plug, eliminating the need for a distributor. This type
of system is more reliable and efficient than a distributor-based system, as
there are fewer moving parts and more direct delivery of the electrical charge
to the spark plugs.
In
conclusion, the ignition system in an automobile plays a critical role in the proper
functioning of the engine. It generates and controls the spark that ignites the
air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber, leading to a controlled explosion
that generates power to drive the vehicle. The ignition system is composed of
several essential components, including the ignition switch, battery, ignition
coil, distributor (in mechanical systems), spark plug wires, spark plugs, and
electronic control modules. There are two main types of ignition systems:
mechanical (or contact breaker) ignition systems and electronic ignition
systems, with the latter being the standard in modern vehicles.
Comments
Post a Comment
Your opinion matters to us, if you have any questions, write it in a comment